Sponsored by Nordic Semiconductor
The release of Bluetooth 6.0 marks a significant milestone in the evolution of Bluetooth technology, introducing Channel Sounding, a groundbreaking feature for precise distance measurement.
With this advancement, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) devices can now estimate distances with a potential of up to centimeter-level accuracy, enabling a wide range of new applications and enhancing existing ones.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into what Bluetooth Channel Sounding is, why it’s important, and how it has the potential to transform industries such as industrial automation, healthcare, consumer electronics, and many more!
The Need for Channel Sounding
Bluetooth technology is already widely used in billions of devices, offering reliable wireless connectivity for data exchange. However, its ability to provide accurate distance measurements has historically been limited, relying on techniques like Received Signal Strength Indication (RSSI) and Direction Finding (AoA/AoD).
Limitations of Existing Methods
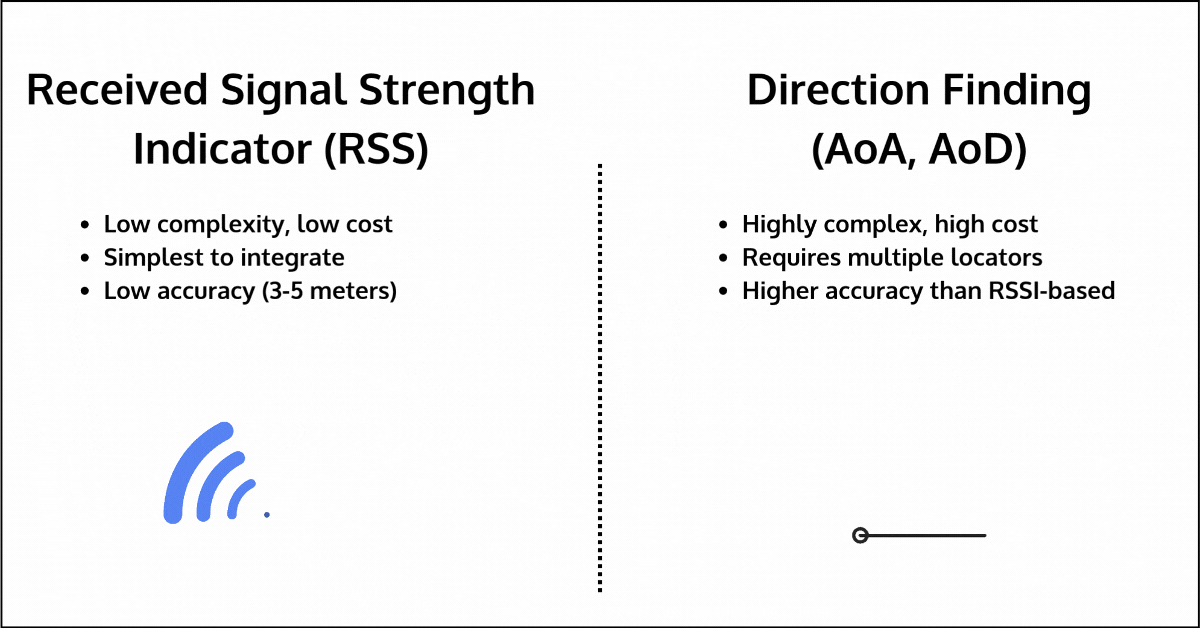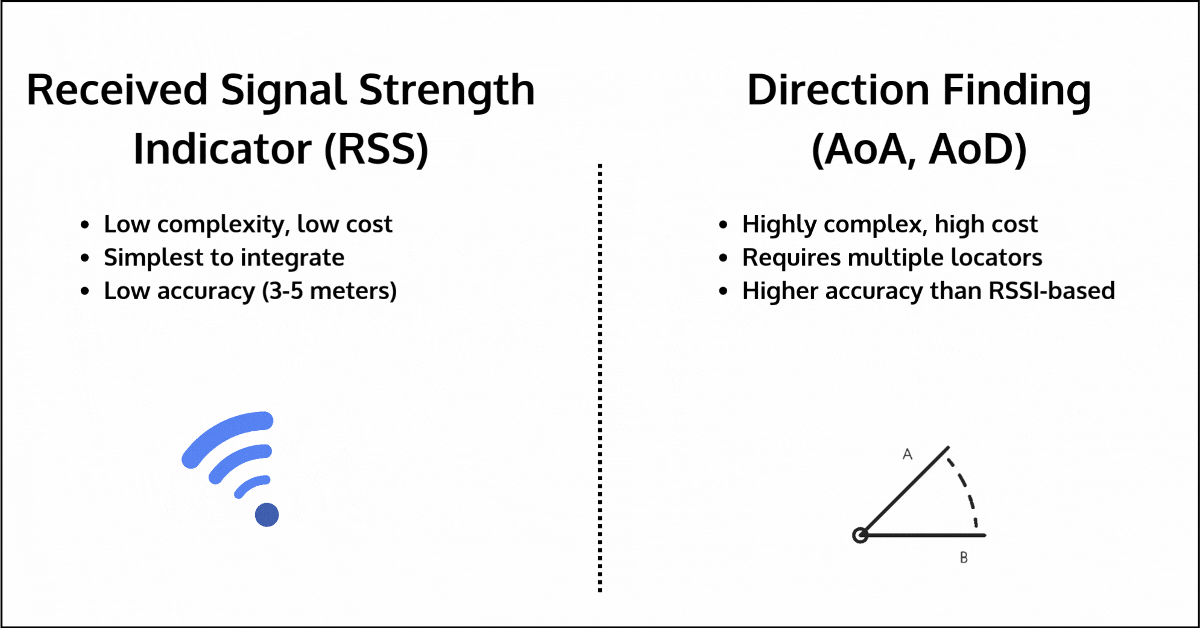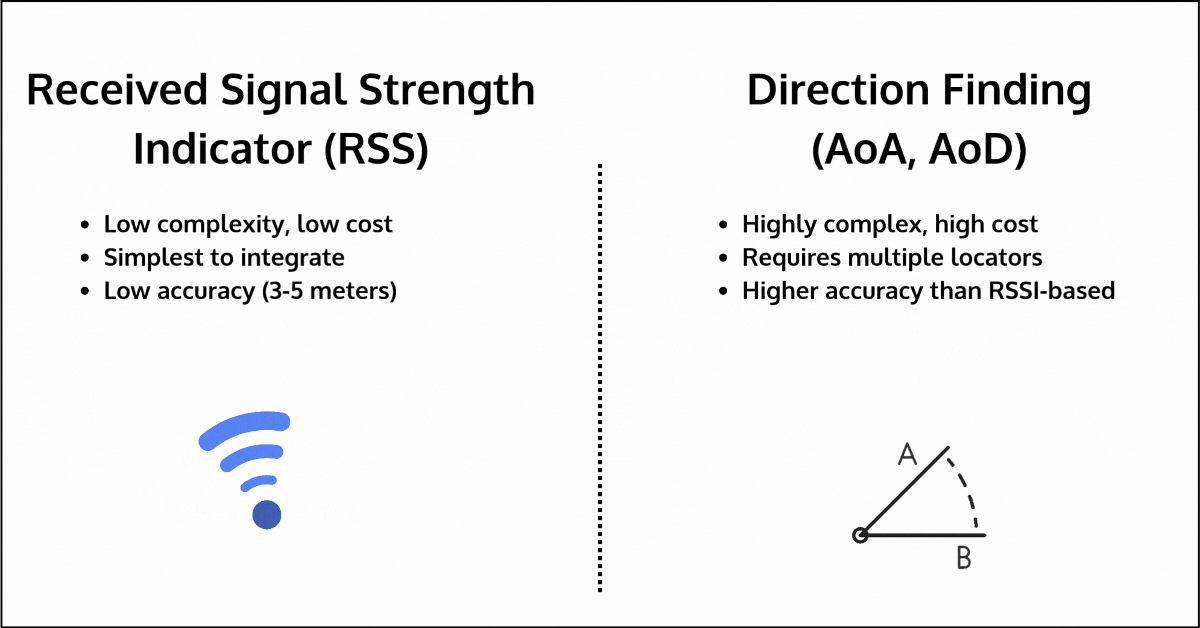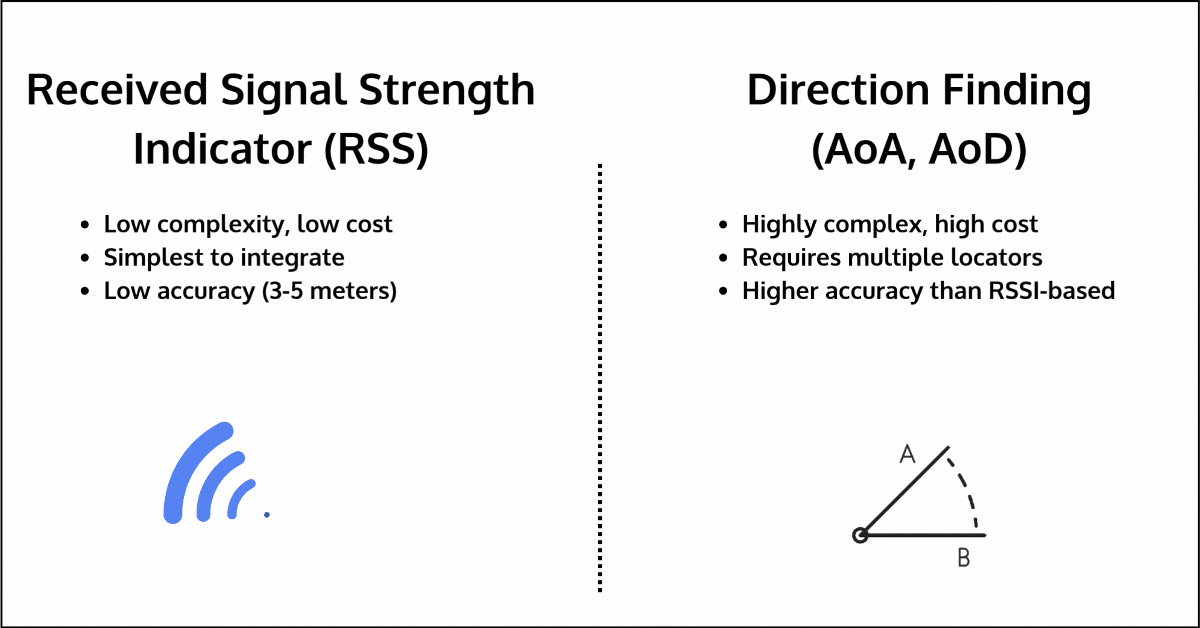
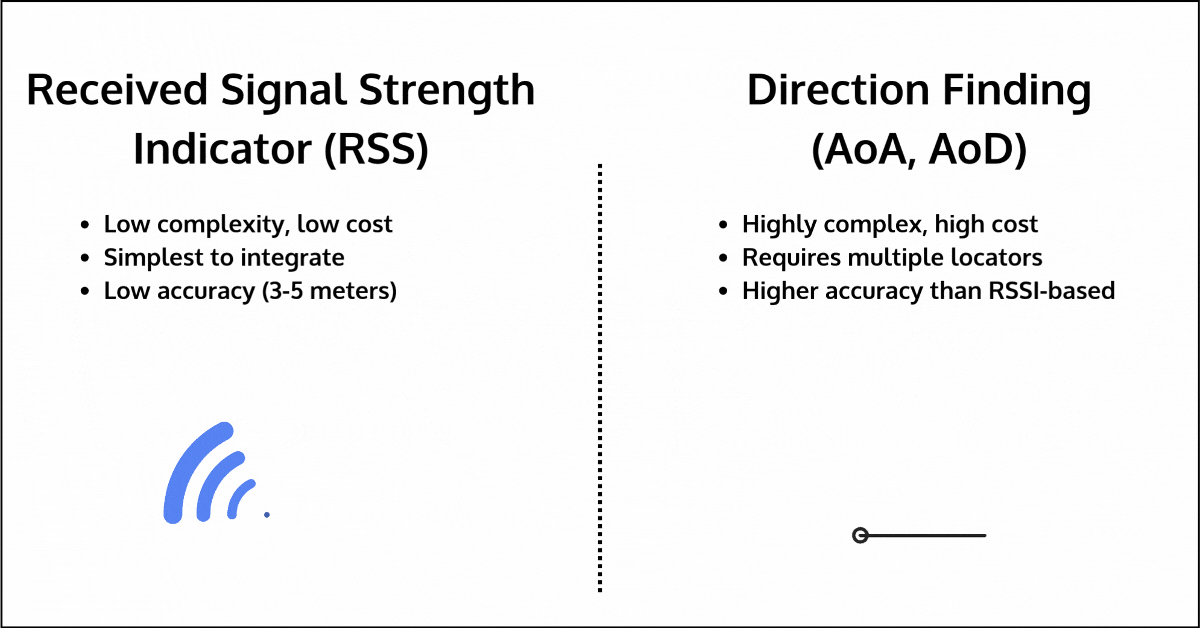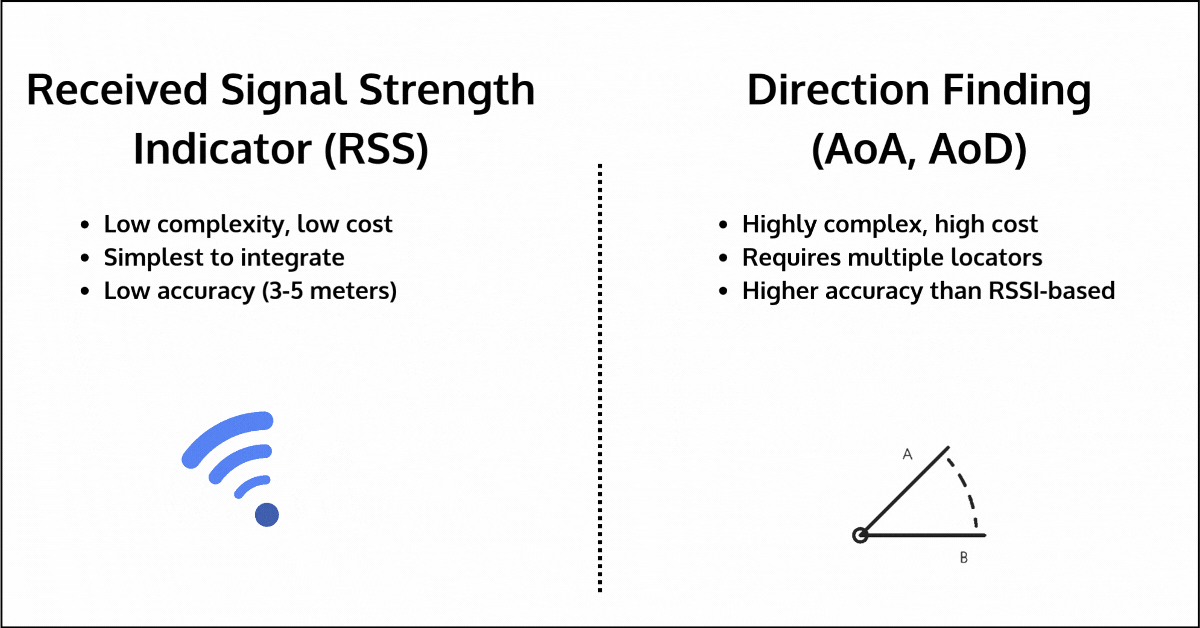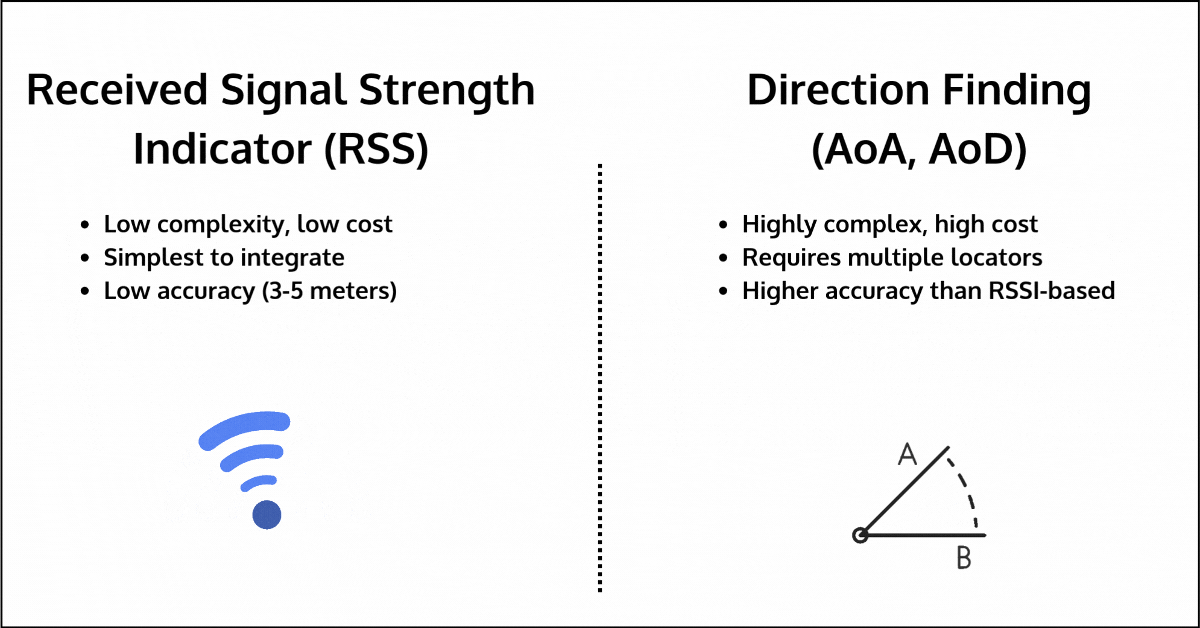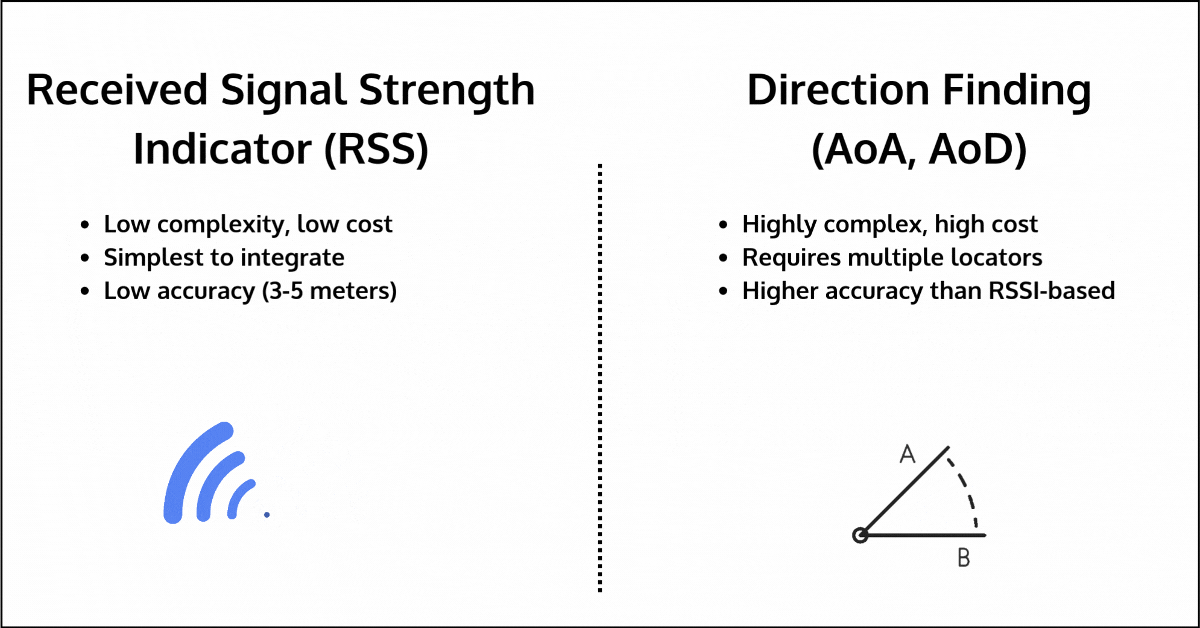
- RSSI (Received Signal Strength Indication): RSSI measures the strength of the signal between two devices to estimate distance. While simple and low-cost, it is highly sensitive to environmental interference, leading to inaccuracies of up to 3-5 meters, especially in environments with walls, human bodies, furniture, or other obstacles. The one advantage it has over other methods is that it’s available for all devices, regardless of communication topology or Bluetooth version used.
- Direction Finding (AoA/AoD): Direction Finding improves upon RSSI by measuring the angle of arrival or departure of signals to estimate distance. However, it requires additional hardware, such as multiple locators, each with antenna arrays, which can significantly increase cost and complexity. Its accuracy can also degrade in multipath environments, where signals reflect off surfaces before reaching their destination.
The Demand for Precision and Security
The rise of IoT, smart devices, and automation has driven the need for highly accurate, secure, cost-effective, and reliable proximity-based solutions. Applications like remote keyless entry systems (RKE) and industrial asset tracking require precise distance measurements that existing methods cannot consistently provide. Channel Sounding fills this gap by offering a robust solution that’s accurate, secure, and low-cost.
What is Bluetooth Channel Sounding?
Bluetooth Channel Sounding is a new feature introduced in Bluetooth 6.0 that enables devices to measure distance with centimeter-level accuracy. It combines advanced signal processing techniques to deliver precise and reliable proximity measurements, even in challenging environments.
At its core, Channel Sounding is designed to:
1. Provide precise distance measurements in real time.
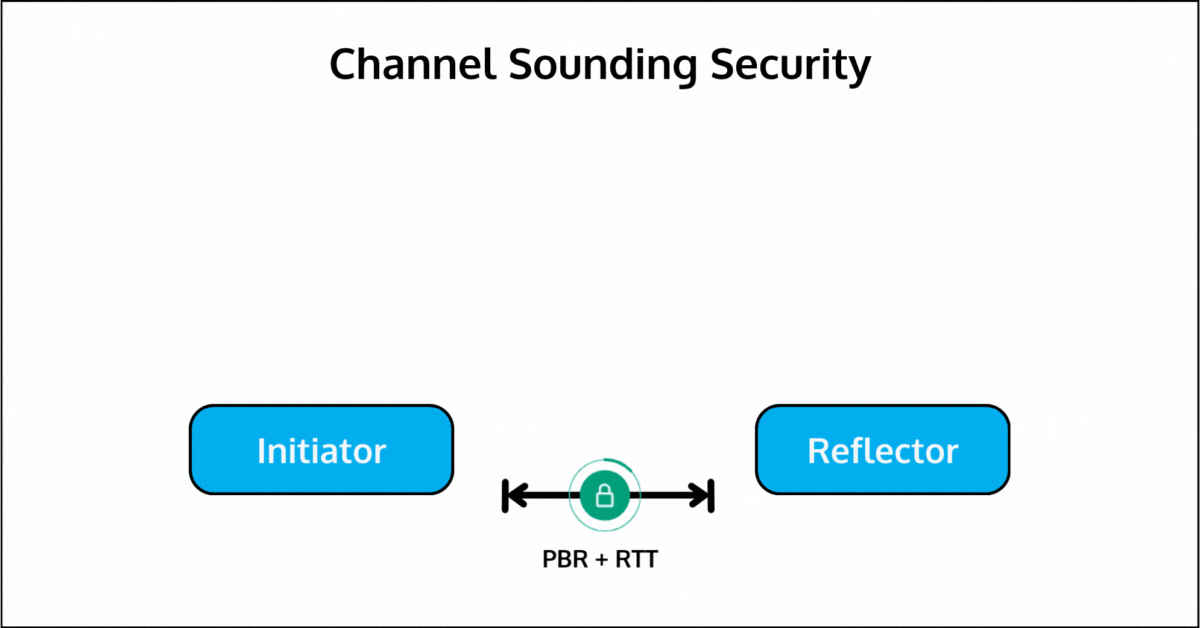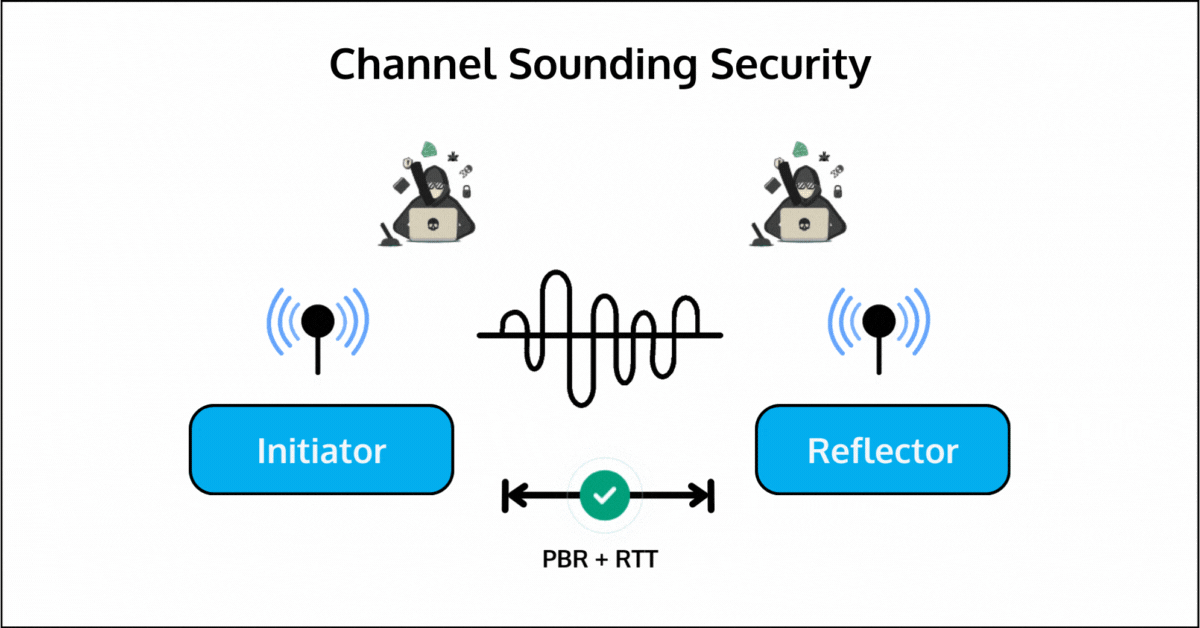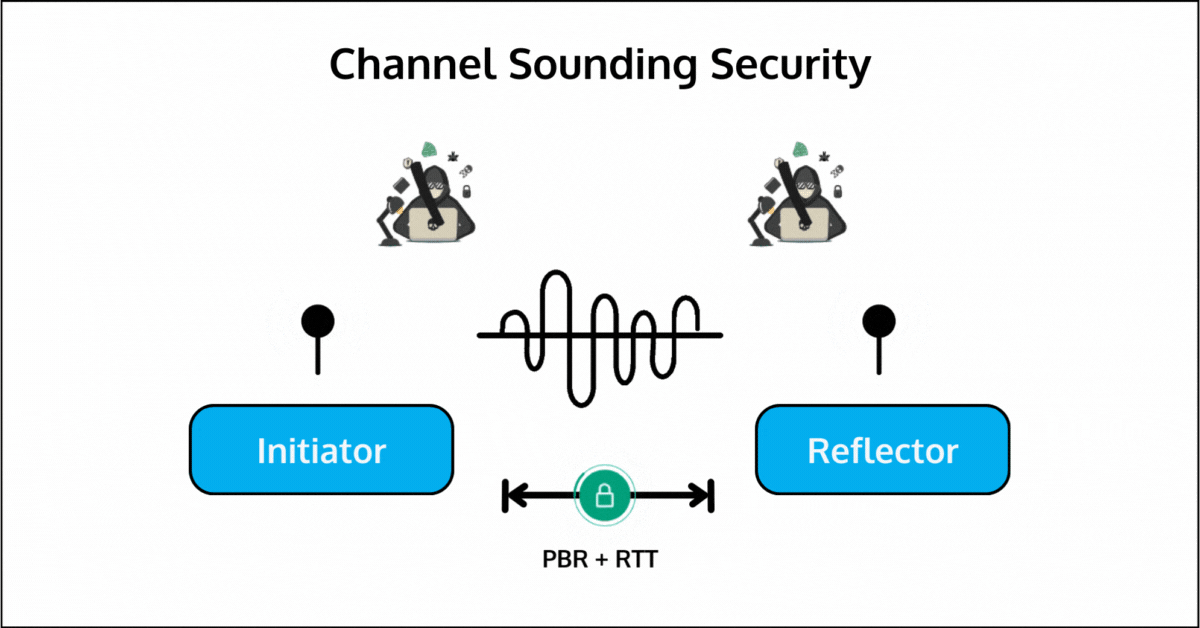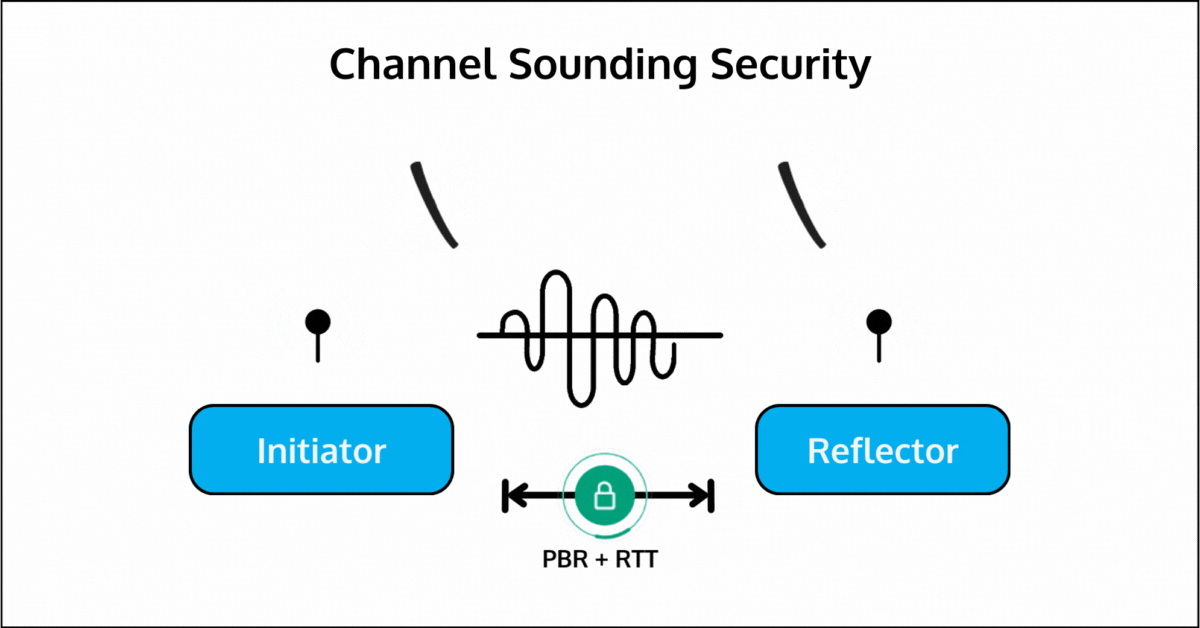
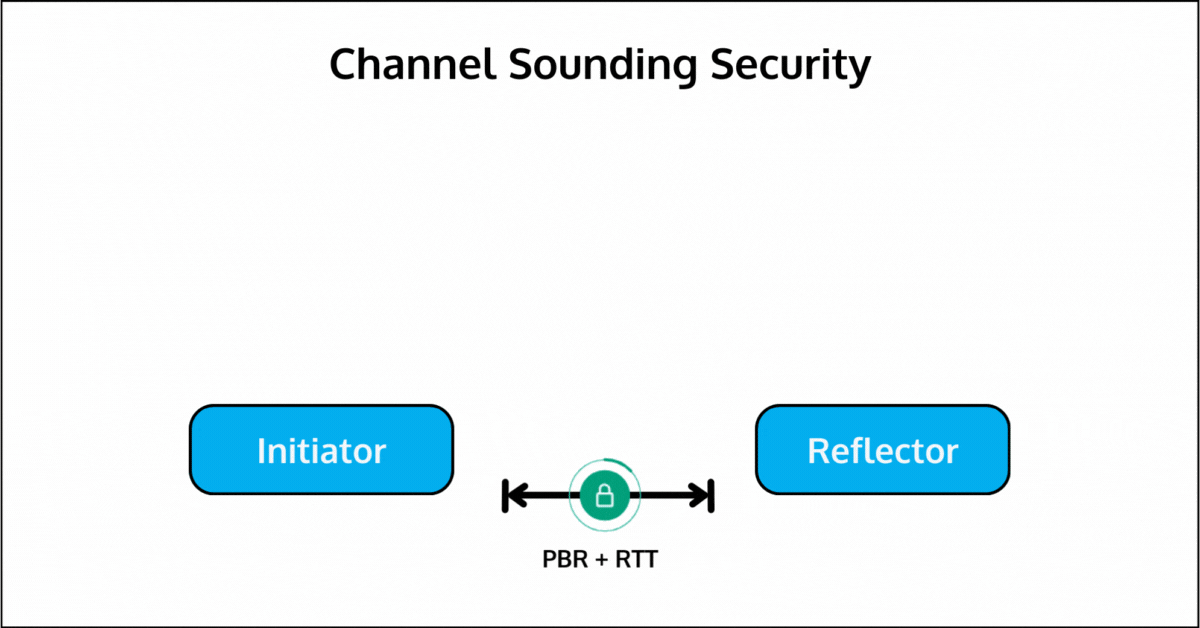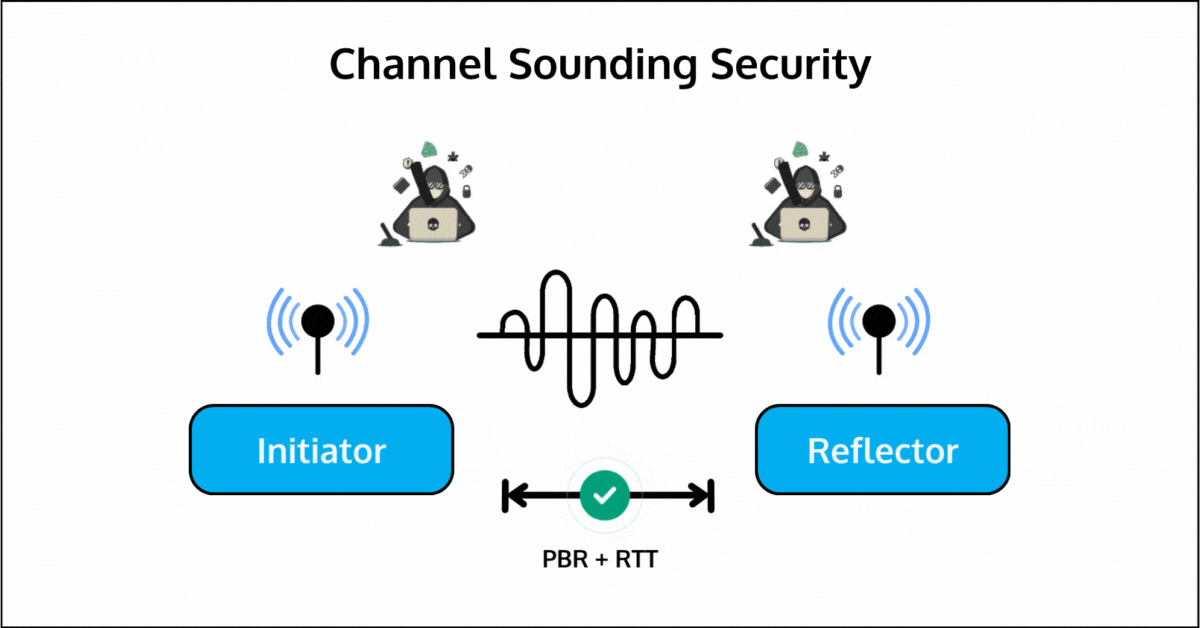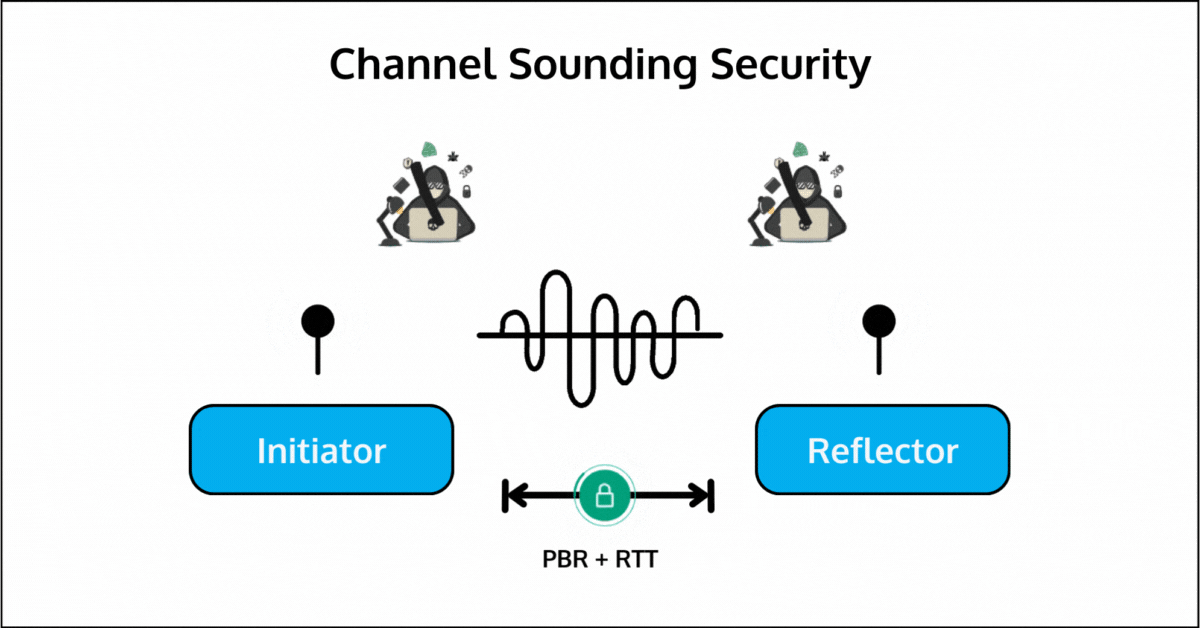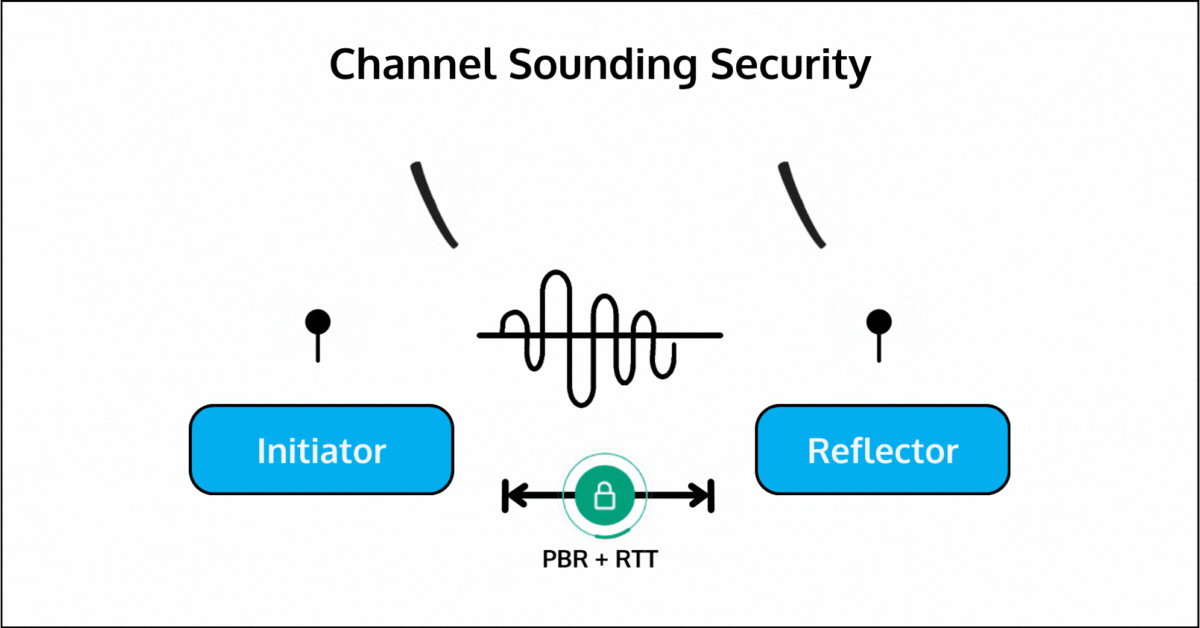
2. Enhance security by preventing attacks like signal spoofing or relay attacks.
3. Operate effectively in complex environments, such as indoor spaces with significant interference or multipath effects.
Channel Sounding achieves this by leveraging two complementary methods:
• Phase-Based Ranging (PBR): Measures the phase differences of signals exchanged between devices to calculate distance.
• Round-Trip Time (RTT): Determines distance by measuring the time it takes for a signal to travel between devices and return.
These methods work together to ensure both accuracy and security. PBR provides accurate distance measurement, and RTT is mainly used to address security. They can be used independently or in combination.
How Bluetooth Channel Sounding Works
Channel Sounding operates in a one-to-one topology, meaning only between connected Bluetooth LE devices. It defines 79 channels in a new PHY (in contrast to 40 channels in the standard LE operation), of which only 72 are used.
One device acts as the Initiator, while the other serves as the Reflector. Each of these roles can be assumed by either the LE Peripheral or Central. It can operate either over a single antenna path (single antenna on each end) or with multiple antenna paths (up to 4—e.g., a dual antenna configuration on each end).

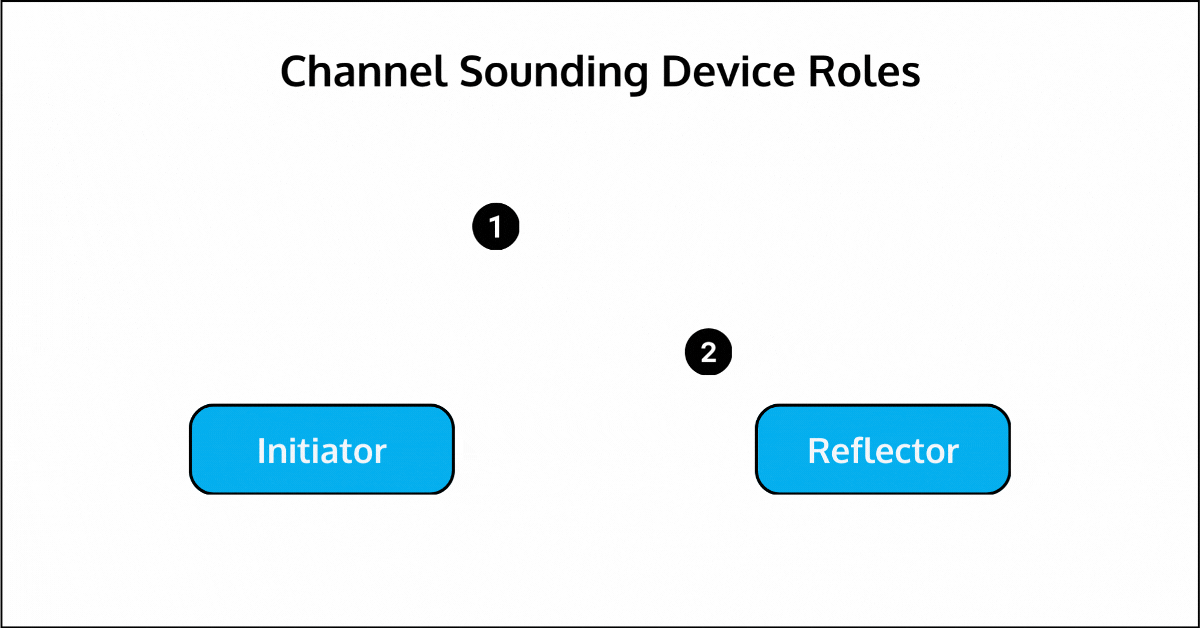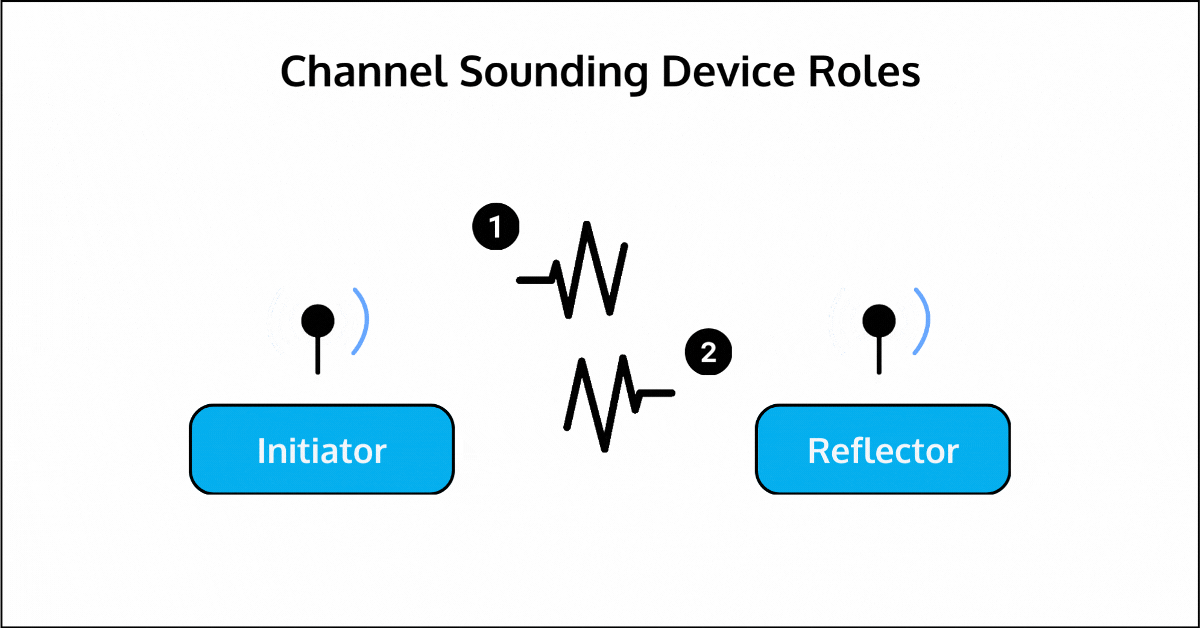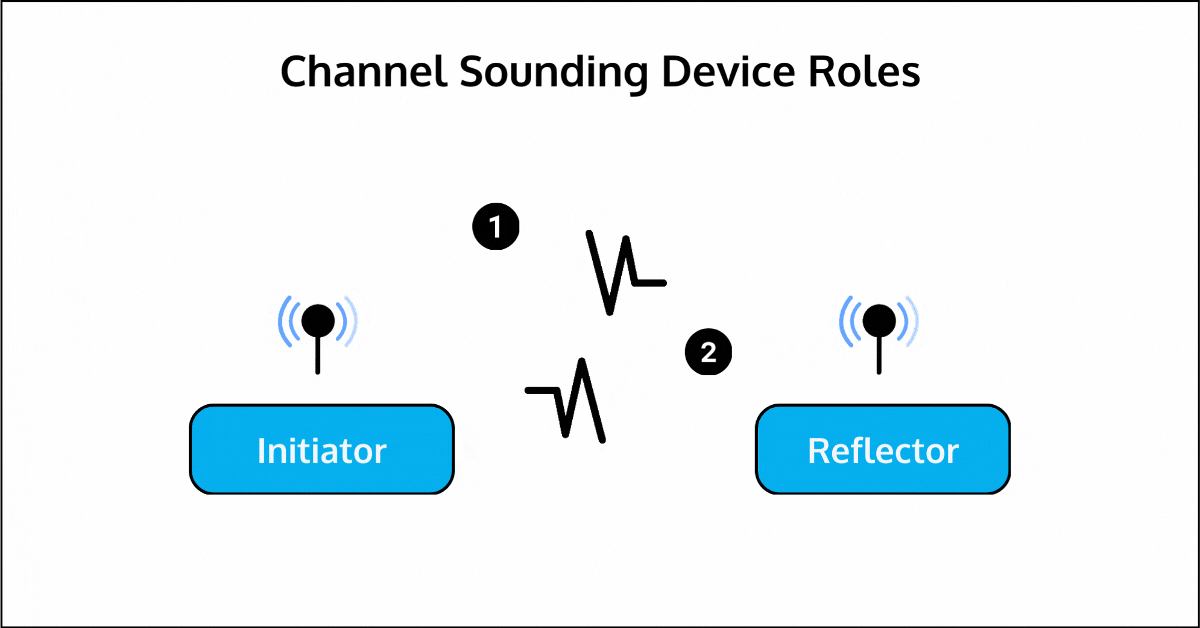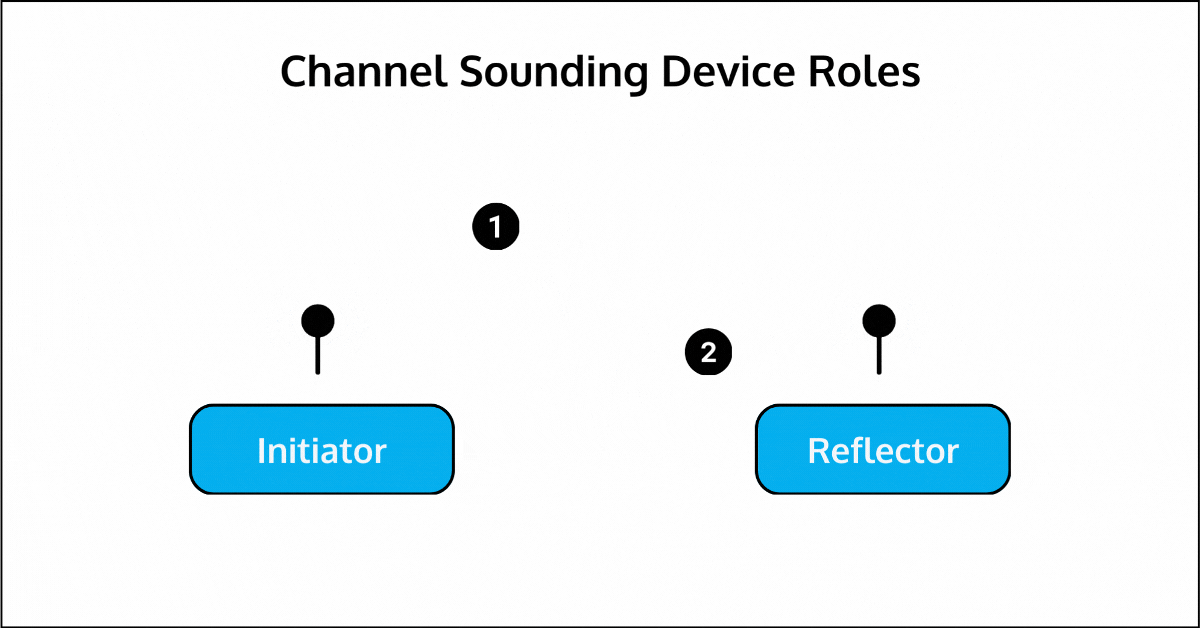
The Channel Sounding process involves several modes of operation, each designed to handle specific aspects of the ranging procedure:
- Mode-0: Synchronization between the devices and basic information exchange.
- Mode-1: Round-Trip Timing (RTT) packets are exchanged to verify and secure the distance measurement.
- Mode-2: Unmodulated tones are transmitted for Phase-Based Ranging (PBR), allowing for highly accurate distance calculations.
- Mode-3 (Optional): Combines RTT and PBR to enhance the measurement’s precision and security.
By utilizing multiple frequency channels within the 2.4 GHz spectrum, Channel Sounding minimizes interference and improves reliability, even in environments with significant signal reflections.
Phase-Based Ranging (PBR)
In simplified terms, the basic operation of PBR is as follows:
- The wavelength is known for a specific frequency
- The transmitter sends a signal at a known phase on a specific frequency
- The receiver then reflects the signal at the exact phase it was received (basically, a continuation of the original signal)
- The phase is then recorded at the transmitter of the signal sent back by the reflector
- This is repeated for different frequencies to account for multi-path
- Based on the phase measurements from the operation over the different frequencies, the distance calculation is performed
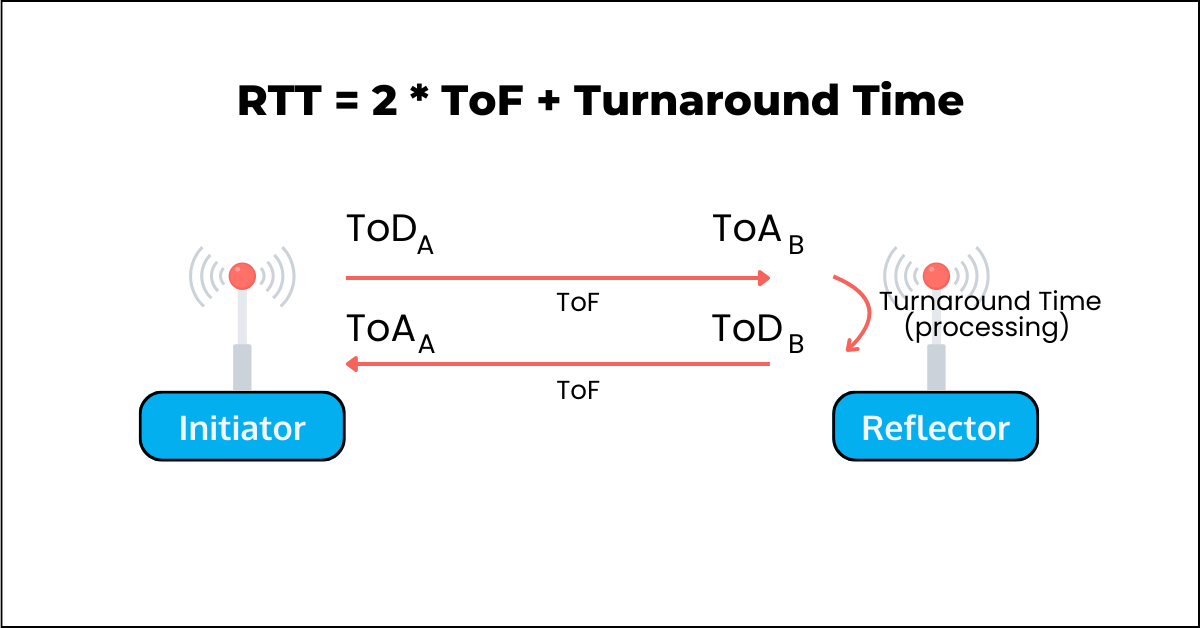
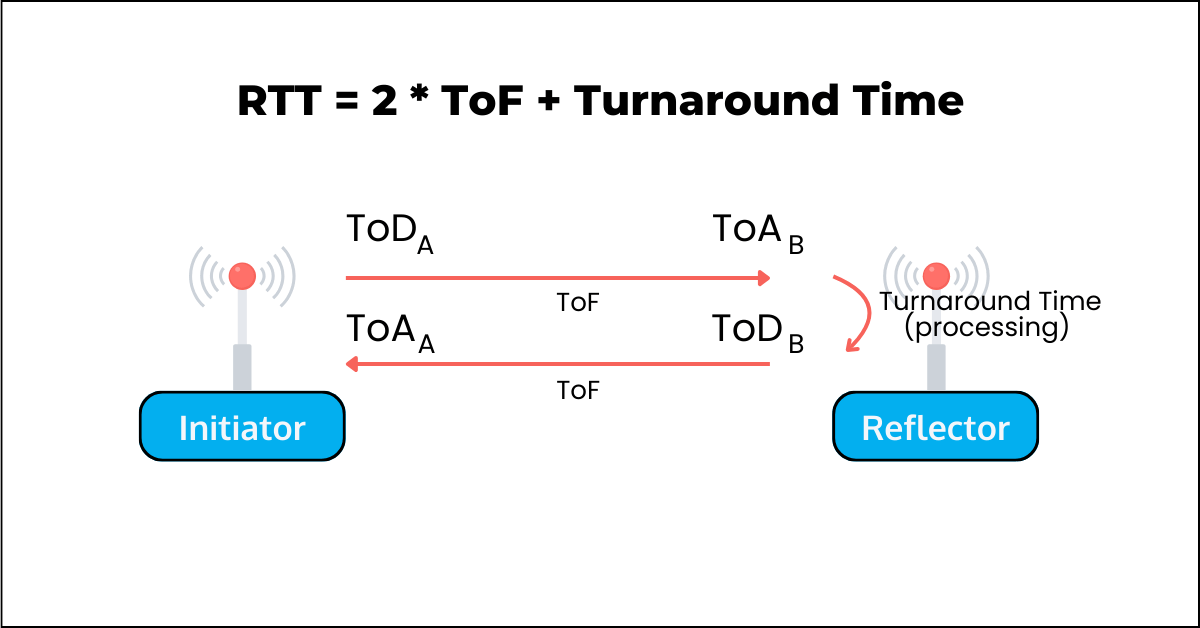
Round-Trip Timing (RTT)
In simplified terms, the basic operation of RTT is as follows:
- Based on the fact that RF transmissions travel at the speed of light, which is constant, the distance between two points is calculated using the time it takes for the signal to travel between these two points
- For round-trip, the time would be for 2x the distance
- The initiator takes into account the turnaround time (which corresponds to the processing time of the signal at the reflector before it is transmitted back to the initiator)
- The figure below showcases how this works.
ToD: Time of Departure, ToA: Time of Arrival, ToF: Time of Flight.
Distance ambiguity refers to the fact that after a certain distance, the difference between the phases will not result in a single distance measurement. This occurs after around 150 m.
To work around this, the second method, Round-Trip Timing (RTT), can be used in conjunction with PBR to provide a more accurate distance measurement.
Distance Calculation Algorithms
One caveat of the Channel Sounding spec is that it does not define the algorithm(s) for the actual distance measurement. Instead, it defines the process and procedures for producing the raw data that goes into the distance calculation algorithm(s). This is the responsibility of the application and higher-level implementation.
Key Benefits of Channel Sounding
1. Increased Accuracy
Channel Sounding enables devices to measure distances with unprecedented precision. This is essential for applications like keyless entry systems, where minor inaccuracies can lead to false activations or security risks.
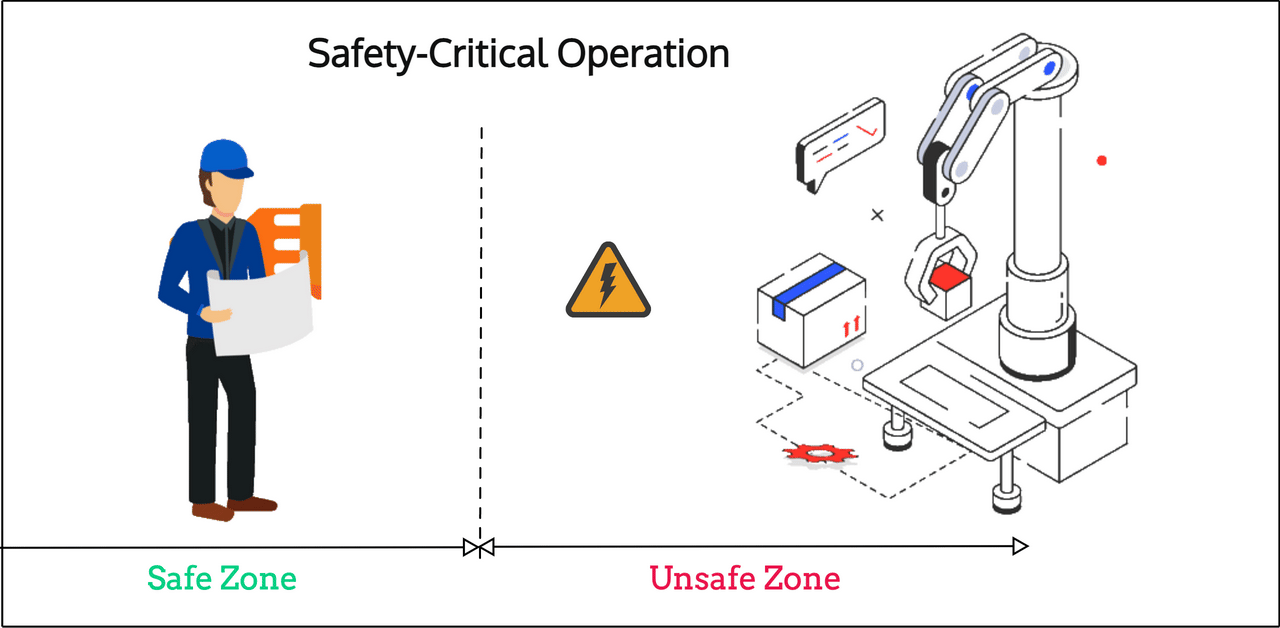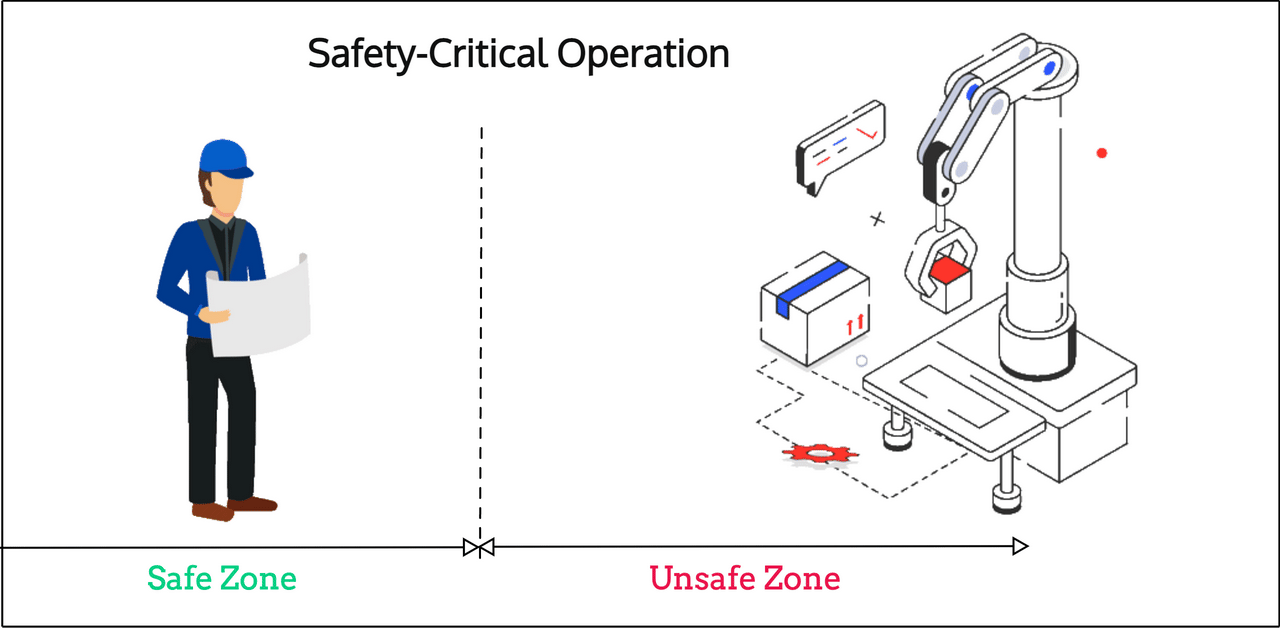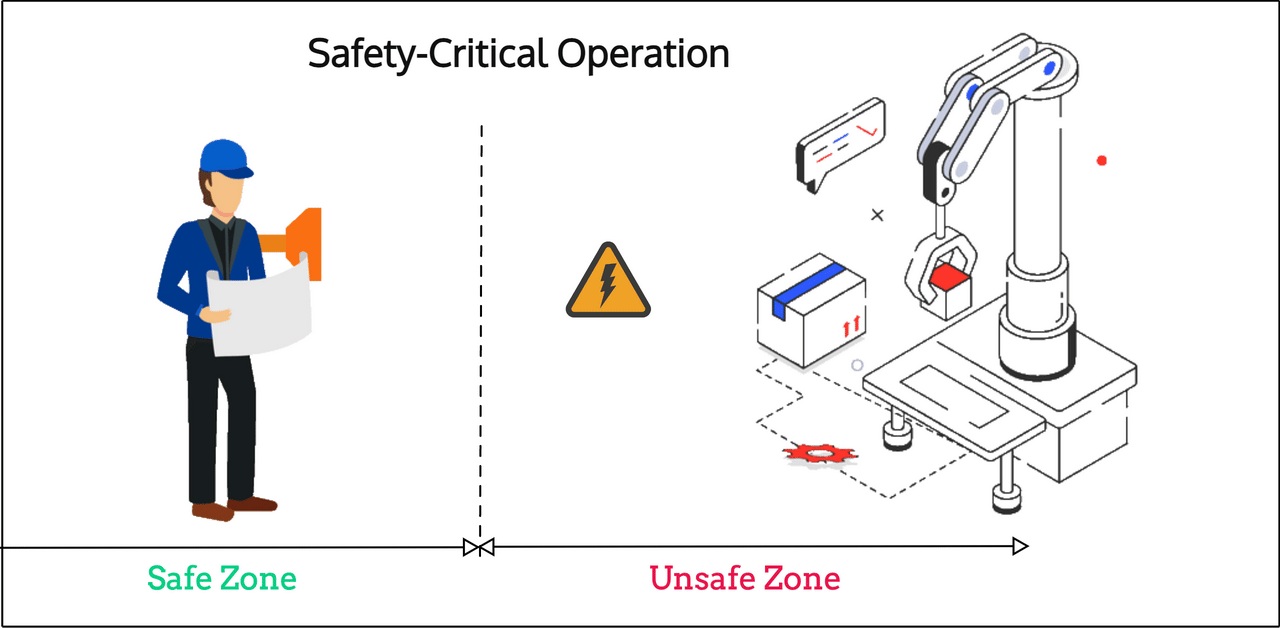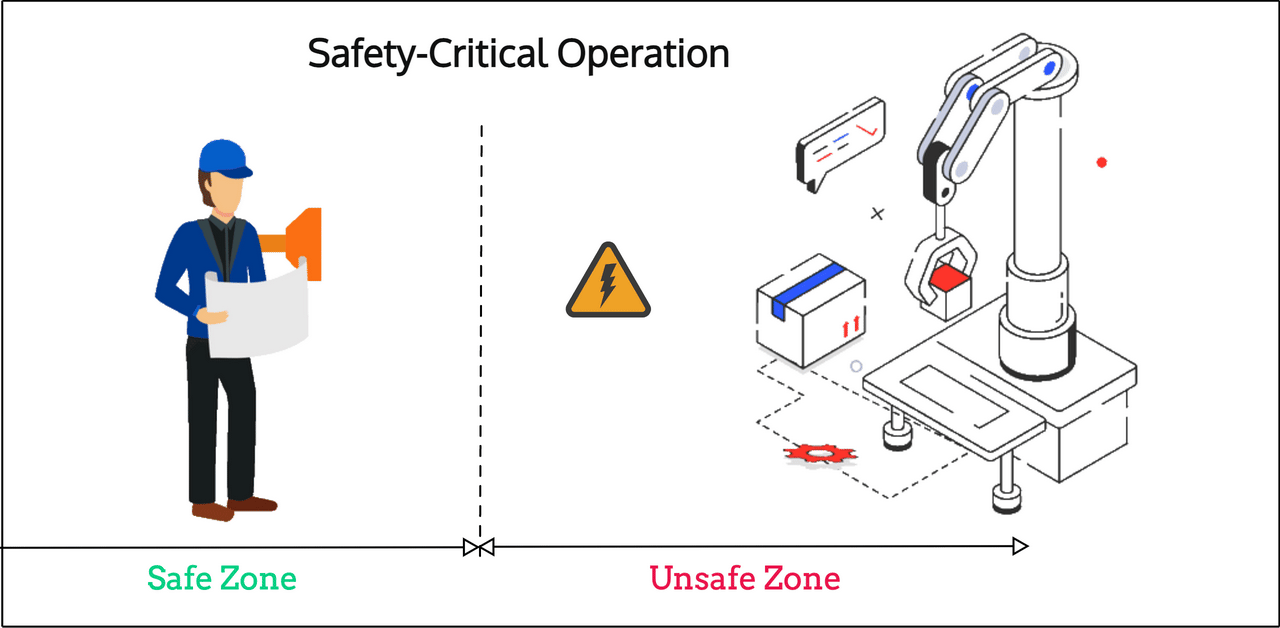
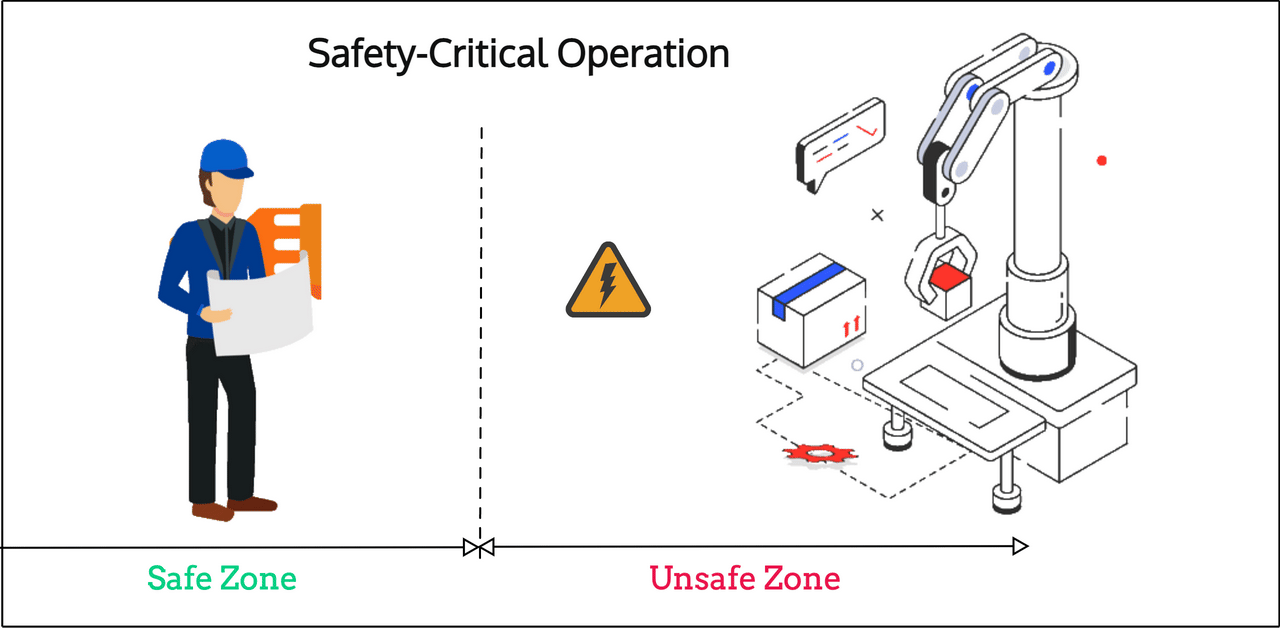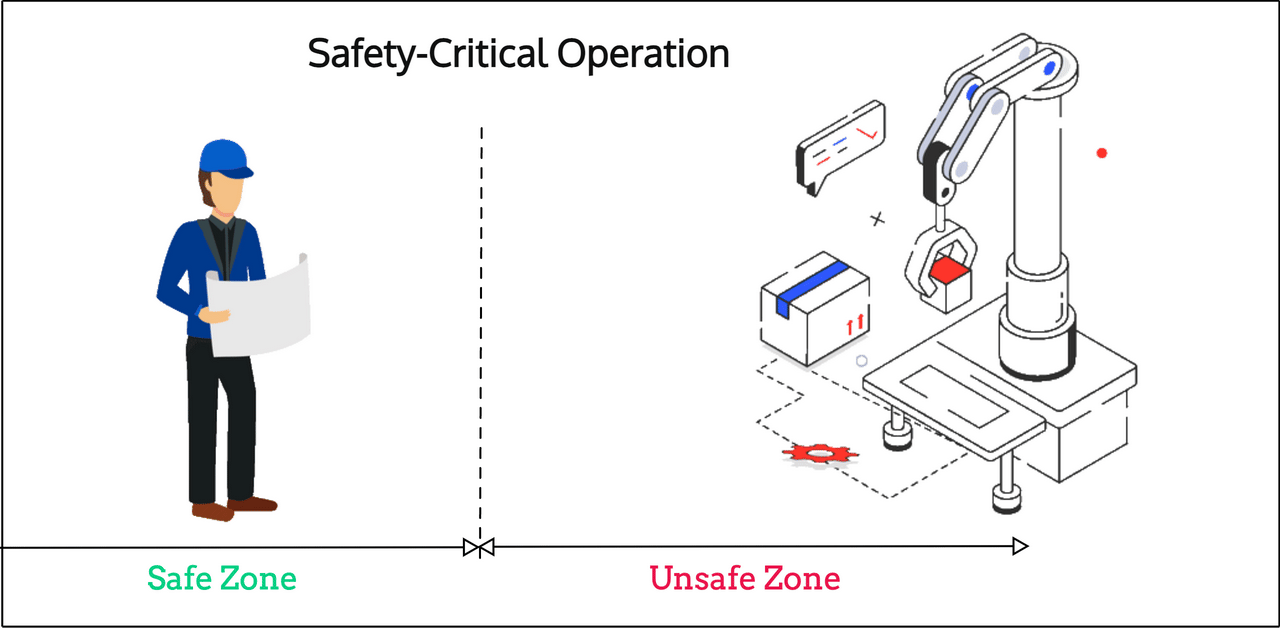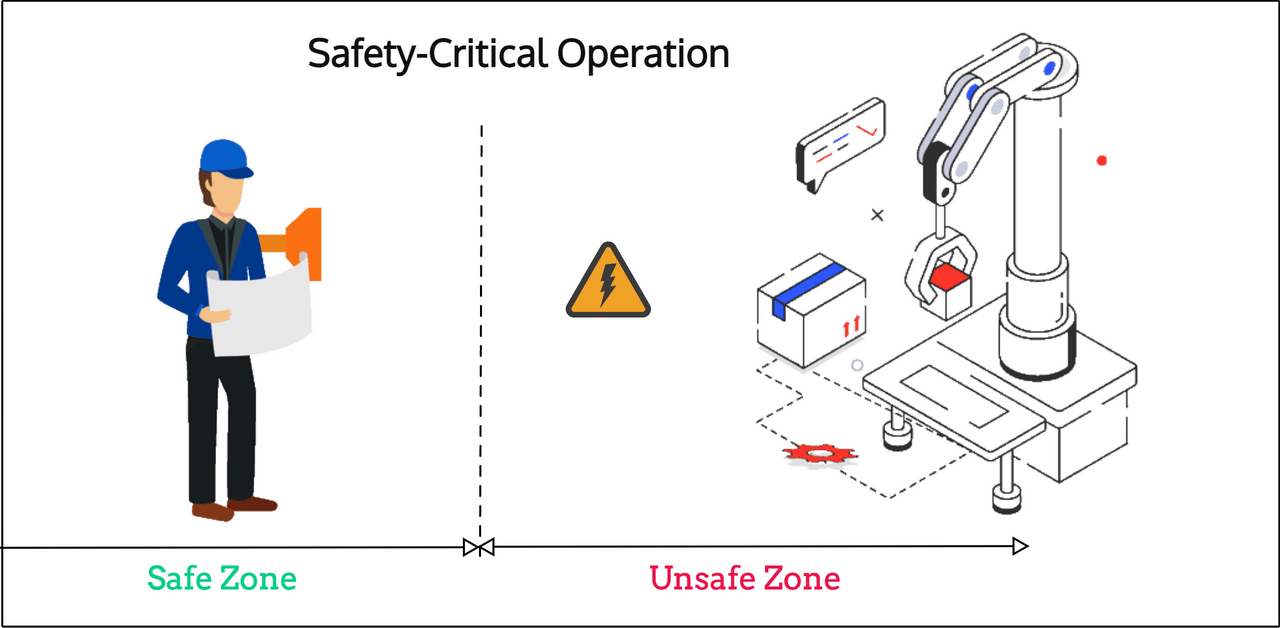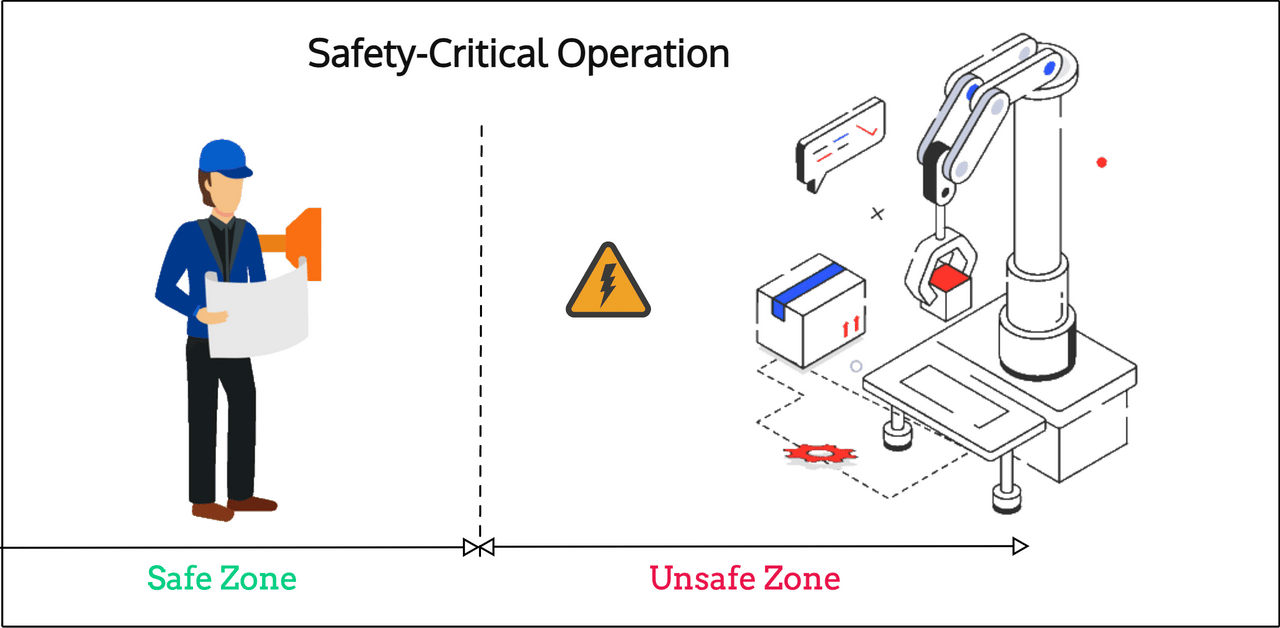
Another application that can highly benefit from Channel Sounding and its more accurate ranging characteristics is in safety-critical operations. Imagine, for example, that a dangerous machine requires its operator to either:
- Operate at a minimum safe distance
- Or operate within a specific proximity/distance of the machine
In both scenarios, Channel Sounding can be used to authenticate the operator and ensure they are within the required distance/zone before operating the machine (typically via their smartphone/tablet/remote control).
2. Enhanced Security
With Round-Trip Time (RTT), Channel Sounding introduces secure distance measurement mechanisms that protect against relay attacks and other forms of signal spoofing. This makes it particularly valuable for proximity-based security applications.
3. Reliable Performance in Complex Environments
Channel Sounding’s ability to operate across multiple frequency channels reduces the impact of interference and multipath effects, ensuring consistent and reliable performance in indoor and industrial settings.
4. Broad Applicability
Channel Sounding is flexible enough to support a wide range of use cases, from consumer electronics and healthcare devices to industrial automation and logistics. Beyond access control, ranging will find use in reliable presence detection, distance estimation, and various other applications yet to be fully explored.
Applications of Bluetooth Channel Sounding
1. Remote Keyless Entry Systems (RKE)
Channel Sounding allows a machine to detect a remote control (or key fob) with high precision, ensuring that a door or any other access control system activates only when the user is within a specific range. This reduces false activations and enhances security.
2. Asset Tracking and Logistics
In industries like warehousing and shipping, accurate location tracking is essential. Channel Sounding enables real-time monitoring of assets, improving efficiency and reducing errors. This application will probably be limited regarding the number of assets that can be monitored since Channel Sounding requires a connection between devices.
3. Collaborative Robotics
Industrial robots often work in environments where precise distance measurement is critical to avoid collisions and enable synchronized operations. Channel Sounding ensures robots can operate safely and effectively in these shared spaces.
4. Healthcare and Medical Devices
Channel Sounding can enhance patient monitoring, equipment tracking, and real-time location systems for critical resources in healthcare applications.
Note: Some of these applications will be limited in terms of the number of devices that can be monitored via Channel Sounding. This is due to the fact that it currently requires a connection between devices. However, this may change in the future if/when connectionless communication becomes supported.
Channel Sounding Support on Nordic Semiconductor SoCs
In terms of support for Channel Sounding on the Nordic Semiconductor platforms, here are a few points to take note of:
- The Softdevice Controller Subsystem and nRF Connect SDK Host for Channel sounding basics are already available in the SDK.
- The existing support provides the bare basics for developers eager to start using this exciting new feature in their projects.
- Samples with a certified Controller and Host will be available later in 2025.
- These samples will provide the easiest way for developers to start designing Channel Sounding applications.
- The functionality will be available on the nRF54L15, to begin with.
The Future of Bluetooth Channel Sounding
As industries continue to adopt proximity-based solutions, the need for accurate and secure distance measurement will only grow. Bluetooth Channel Sounding is poised to become a cornerstone technology, unlocking new possibilities in IoT, automation, consumer electronics, and beyond.
Future developments may focus on:
- Improving energy efficiency for battery-powered devices.
- Expanding support across mobile platforms to enable seamless integration.
- Enabling more complex topologies for multi-device environments.
Major potential with Channel Sounding will be achieved if/once it becomes supported on smartphones, which seems very promising at the moment!
Conclusion
Bluetooth Channel Sounding is a transformative technology that addresses the limitations of traditional distance measurement methods, offering unmatched accuracy, robust security, and reliable performance in real-world environments. From enabling smarter keyless entry systems to enhancing industrial automation, its applications are as diverse as they are impactful.
As Bluetooth technology continues to evolve, Channel Sounding is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of wireless connectivity, bridging the gap between precision and practicality in a wide range of industries.


